If you’re interested in learning more about insulin resistance and how it can affect your health, you’ve come to the right place. In this blog post, we’ll explore what insulin resistance is, what causes it, and how it can be managed. By the end of this post, you should have a better understanding of this important topic. So let’s get started!
What is Insulin Resistance?
In order to understand insulin resistance, we must first understand what insulin is. Insulin is a hormone that helps our cells use glucose for energy. Glucose is a type of sugar that comes from the food we eat. When we eat foods that contain carbohydrates (such as bread, pasta, rice, potatoes, and cereals), our bodies break them down into glucose. The glucose then enters our bloodstream and inflation rises. In response to this rise in blood sugar, our pancreas produces insulin. The role of insulin is to move the glucose from our bloodstream into our cells so that it can be used for energy.
If you have insulin resistance, this process does not happen effectively. The pancreas produces insulin but the cells are resistant to it and do not take in the glucose as they should. As a result, the level of glucose in your bloodstream becomes elevated. Over time, if not managed properly, this can lead to type 2 diabetes.
Causes of Insulin Resistance
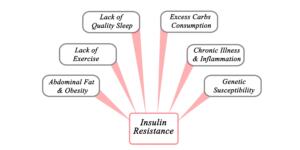
There are a number of things that can contribute to insulin resistance. These include:
• Unhealthy diet: A diet high in refined carbs and sugar can lead to weight gain and increased inflammation, both of which contribute to insulin resistance.
• Lack of exercise: Exercise helps improve sensitivity to insulin.
• Certain medical conditions: Conditions such as polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), sleep apnea, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) have all been linked to insulin resistance.
• Medications: Some medications such as steroids can increase insulin resistance.
• Age: Our ability to process glucose declines with age, which can lead to insulin resistance.
• Family history: If someone in your family has type 2 diabetes, you may be more likely to develop insulin resistance yourself.
Managing Insulin Resistance
If you think you may be at risk for developing insulin resistance or if you have already been diagnosed with the condition, there are things you can do to manage it. These include:
• Eating a healthy diet: Eating lots of fresh fruits and vegetables, lean protein, whole grains, and healthy fats can help promote weight loss and reduce inflammation.
• Exercising regularly: Exercise helps improve sensitivity to insulin and promotes weight loss. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate exercise most days of the week.
• Managing stress: Chronic stress can raise cortisol levels and contribute to weight gain—both of which increase the risk of developing insulin resistance. Finding ways to manage stress through yoga, meditation, or deep breathing can help lower your risk.
These lifestyle changes can go a long way toward keeping your cells sensitive to insulin and helping you avoid diabetes or prediabetes. However, if you have already been diagnosed with either condition, there are still steps you can take to manage your condition and improve your health. These include working with a healthcare professional to create a treatment plan that is right for you. Some people may need medication in addition to lifestyle changes in order to get their blood sugar under control.
If you think you may be at risk for insulin resistance, talk to your healthcare professional today about ways you can lower your risk and improve your health! Share this information with your friends and loved ones who may also be at risk so they can take steps to protect their health as well!

